Think your IT team has cybersecurity covered? Think again. Every employee is a key player in safeguarding your organization from digital threats. Without adequate training, you might inadvertently become a target for cybercriminals who exploit human error.
From falling prey to phishing schemes to using easily guessable passwords, the risks are real. However, with the right training, you can evolve from a potential vulnerability to a strong line of defense.
So, what skills and knowledge do you need to become a cybersecurity asset for your organization?
Let’s explore the essentials that can help you protect sensitive information and contribute to a safer workplace.
Key Takeaways
- Employees are often the weakest link in cybersecurity, making training essential to reduce human error risks.
- Training helps staff recognize and respond to phishing attempts and social engineering tactics.
- Properly trained employees can effectively implement data protection best practices in their daily work.
- Cybersecurity training ensures staff understand incident response procedures and can report issues promptly.
- Ongoing employee education addresses evolving cyber threats and reinforces a culture of security awareness.
Human Error in Cyber Attacks
One of the biggest threats to an organization’s cybersecurity isn’t sophisticated hacking tools or advanced malware—it’s the people within the company itself. Human error accounts for a considerable portion of successful cyber attacks, making employee training essential for maintaining a robust security posture.
You might be surprised to learn that seemingly innocuous actions can lead to severe breaches. Falling for phishing emails, using weak passwords, or carelessly handling sensitive data are common mistakes that cybercriminals exploit. These errors often stem from a lack of awareness or complacency rather than malicious intent.
To combat this vulnerability, you need to foster a culture of cybersecurity awareness. This means educating your staff about the latest threats, teaching them to recognize social engineering tactics, and instilling best practices for data handling.
Regular training sessions, simulated phishing exercises, and clear security protocols can considerably reduce the risk of human-induced breaches.
Recognizing Phishing and Social Engineering
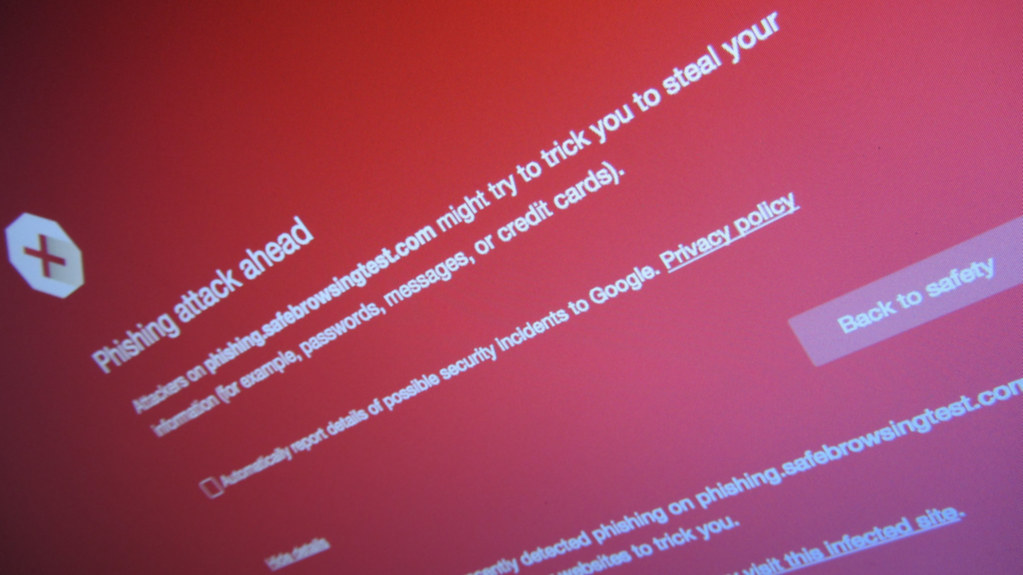
Recognizing phishing and social engineering attacks is a key component of effective cybersecurity training. You’ll need to learn how to spot suspicious emails, messages, and phone calls that aim to trick you into revealing sensitive information or granting unauthorized access.
Look for red flags like urgent requests, unexpected attachments, or links to unfamiliar websites. Be wary of emails asking you to verify account details or update passwords, especially if they create a sense of urgency. Always double-check the sender’s email address for subtle misspellings or unusual domains.
Social engineering tactics often exploit human psychology, so you’ll need to be cautious of unsolicited requests for information, even if they seem to come from authority figures. Don’t be afraid to verify requests through official channels before complying.
Learn to recognize common phishing techniques like spoofed websites, fake login pages, and deceptive pop-ups. Use multi-factor authentication whenever possible to add an extra layer of security.
Data Protection Best Practices

To protect sensitive data effectively, you’ll need to implement a range of best practices in your daily work routine.
Start by using strong, unique passwords for all your accounts and enable two-factor authentication whenever possible. Regularly update your software and operating systems to patch vulnerabilities and protect against the latest threats.
Be cautious when handling sensitive information. Encrypt confidential files before sending them and use secure file-sharing methods. Avoid storing sensitive data on personal devices or public cloud services. Instead, utilize company-approved storage solutions with proper access controls.
When working remotely, always use a VPN to secure your connection. Be mindful of your surroundings when accessing sensitive information in public spaces. Lock your computer screen when you’re away from your desk, even for short periods.
Regularly back up important data and test your recovery processes. Familiarize yourself with your company’s data classification policies and handle information accordingly.
Report any suspicious activities or potential data breaches to your IT department immediately. By following these practices consistently, you’ll greatly reduce the risk of data breaches and protect your organization’s valuable information assets.
Incident Response and Reporting

While data protection best practices help prevent incidents, you must also be prepared to respond effectively when cybersecurity issues arise. Your organization should have a clear incident response plan that outlines the steps to take when a security breach occurs.
As an employee, you need to know your role in this plan and how to report suspicious activities or potential breaches. When you encounter a potential cybersecurity threat, don’t hesitate to report it immediately to your IT department or designated security team. Time is essential in mitigating the impact of an attack.
Learn to recognize common signs of a breach, such as unusual system behavior, unexpected pop-ups, or unauthorized access attempts. Keep detailed notes about any incidents you observe, including dates, times, and specific actions taken.
Your organization may use specific reporting tools or procedures. Familiarize yourself with these processes and practice using them.
Remember, incident response isn’t just about technology; it’s also about communication. Be prepared to collaborate with colleagues and management during a crisis.
Continuous Learning and Adaptation

Cybersecurity threats evolve rapidly, making continuous learning and adaptation essential for employees. You must stay informed about the latest attack methods, vulnerabilities, and defense strategies to protect your organization effectively. Regular updates to your cybersecurity knowledge help you identify and respond to new threats quickly.
Engage in ongoing training programs that focus on emerging trends and technologies. Participate in workshops, webinars, and online courses to enhance your skills. You’ll learn about advanced phishing techniques, ransomware variants, and social engineering tactics that cybercriminals use to exploit human vulnerabilities.
Adapt your behavior based on new information and best practices. Apply lessons learned from past incidents to improve your security posture. Stay curious and ask questions when you encounter unfamiliar situations or potential risks.
Collaborate with your IT team and share insights with colleagues to create a culture of continuous improvement. By embracing lifelong learning in cybersecurity, you’ll contribute to your organization’s resilience against evolving threats.
Conclusion
You’ve seen why employee training is essential for cybersecurity. It’s your responsibility to stay informed and vigilant. By understanding human error, recognizing threats, and following best practices, you’re strengthening your organization’s defenses. Remember, cybersecurity isn’t a one-time effort; it’s an ongoing process. Stay committed to continuous learning and adaptation. Your actions matter, and with proper training, you’ll play an important role in safeguarding your company’s digital assets.

